

Structural Heart Disease
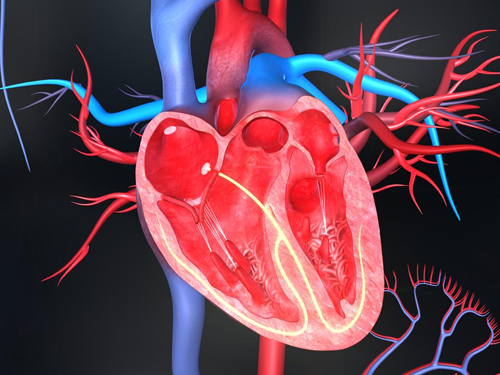
Structural heart disease refers to abnormalities in the heart’s structure, including the valves, walls, or chambers. These conditions can be congenital (present at birth) or acquired (develop over time) and can cause symptoms like shortness of breath, palpitations, and fatigue. Treatment options include monitoring, medications, and, when necessary, surgical interventions like valve repair or replacement.
Common Types -
1) Congenital Heart Defects: Such as atrial septal defects (ASD) or ventricular septal defects (VSD).
2) Heart Valve Disease: Conditions like aortic or mitral valve stenosis or regurgitation.
3) Cardiomyopathy: Conditions that affect the heart muscle, such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Symptoms -
1) Shortness of breath
2) Fatigue or exercise intolerance
3) Heart palpitations or irregular heartbeat
4) Swelling in the feet, ankles, hands, or abdomen
5) Dizziness or fainting
6) Chest pain or tightness
Treatment Options -
1) Monitoring: Mild cases may only require ongoing observation.
2) Medications: To control symptoms and improve heart function.
3) Minimally Invasive Procedures: Techniques like TAVR or mitral valve clipping.
4) Surgical Procedures: Open-heart surgery may be necessary in more severe cases.
5) Heart Transplant: Considered for severe structural defects.